Bill that could make TikTok unavailable in the US advances quickly in the House
- By 6122ee467d22433199917c7d
- •
- 08 Mar, 2024
Bill that could make TikTok unavailable in the US advances quickly in the House

A bill that could lead to the popular video-sharing app TikTok being unavailable in the United States is quickly gaining traction in the House as lawmakers voice concerns about the potential for the platform to surveil and manipulate Americans.
The measure gained the support of House Speaker Mike Johnson and could soon come up for a full vote in the House. The bill advanced out of committee Thursday in a unanimous bipartisan vote — 50-0.
The White House has provided technical support in the drafting of the bill, though White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre said the TikTok legislation “still needs some work” to get to a place where President Joe Biden would endorse it.
The bill takes a two-pronged approach. First, it requires ByteDance Ltd., which is based in Beijing, to divest TikTok and other applications it controls within 180 days of enactment of the bill or those applications will be prohibited in the United States. Second, it creates a narrow process to let the executive branch prohibit access to an app owned by a foreign adversary if it poses a threat to national security.
“It’s an important, bipartisan measure to take on China, our largest geopolitical foe, which is actively undermining our economy and security,” Johnson said Thursday.
Some lawmakers and critics of TikTok have argued the Chinese government could force the company to share data on American users. TikTok says it has never done that and wouldn’t do so if asked. The U.S. government also hasn’t provided evidence of that happening.
Critics also claim the app could be used to spread misinformation beneficial to Beijing.
Former President Donald Trump attempted to ban TikTok through executive order, but the courts blocked the action after TikTok sued, arguing such actions would violate free speech and due process rights.
TikTok raised similar concerns about the legislation gaining momentum in the House.
“This bill is an outright ban of TikTok, no matter how much the authors try to disguise it. This legislation will trample the First Amendment rights of 170 million Americans and deprive 5 million small businesses of a platform they rely on to grow and create jobs,” the company said in a prepared statement.
The bill’s author, Rep. Mike Gallagher, the Republican chairman of a special House committee focused on China, rejected TikTok’s assertion of a ban. Rather, he said it’s an effort to force a change in TikTok’s ownership. He also took issue with TikTok urging some users to call their representatives and urge them to vote no on the bill.
The notification urged TikTok users to “speak up now — before your government strips 170 million Americans of their Constitutional right to free expression.” The notification also warned that the “ban” of TikTok would damage millions of businesses and destroy the lives of countless creators around the country.
TikTok users responded by flooding the offices of lawmakers with telephone calls. Some offices even shut off their phones because of the onslaught. A congressional aide not authorized to speak on the matter publicly said that lawmakers on the committee voting on the bill Thursday as well as others were inundated with calls.
“Today, it’s about our bill and it’s about intimidating members considering that bill, but tomorrow it could be misinformation or lies about an election, about a war, about any number of things,” Gallagher said. “This is why we can’t take a chance on having a dominant news platform in America controlled or owned by a company that is behold to the Chinese Communist Party, our foremost adversary.”
The bill comes about one year after TikTok’s CEO was grilled for hours by skeptical lawmakers on the House Energy and Commerce Committee concerned about data security and the distribution of harmful content. That same committee met Thursday to debate and vote on the bill.
Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers, the committee’s Republican chair, said TikTok’s access to so many Americans makes it a valuable propaganda tool for the Chinese government to exploit. She also noted that its parent company ByteDance is currently under investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice for surveilling American journalists.
“Through this access, the app is able to collect nearly every data point imaginable, from people’s location, to what they search on their devices, who they are connecting with, and other forms of sensitive information,” Rodgers said.
To assuage concerns from lawmakers, TikTok has promised to wall off U.S. user data from its parent company through a separate entity run independently from ByteDance and monitored by outside observers. TikTok says new user data is currently being stored on servers maintained by the software company Oracle.
The American Civil Liberties Union and other free speech advocacy groups urged lawmakers to reject the TikTok bill, saying in a letter to the Energy and Commerce Committee’s leadership that “passing this legislation would trample on the constitutional right to freedom of speech of millions of people in the United States.”
Biden’s reelection campaign has opened a TikTok account as a way to boost its appeal with young voters, even as his administration continued to raise security concerns about whether the popular social media app might be sharing user data with China’s communist government.
Jean-Pierre said the White House welcomes lawmakers’ efforts on the TikTok legislation, but lawmakers need to continue work on it.
“Once it gets to a place where we think .. it’s on legal standing and it’s in a place where it can get out of Congress, then the president would sign it,” she told reporters on Wednesday during the daily White House briefing.
She also defended the White House’s efforts to limit the dangers of TikTok, even as the president engages with influencers on the social-media platform and his campaign hosts a TikTok account.
“We are going to try to meet the America people where they are,” Jean-Pierre said. “We are trying to reach everyone. The president is the president for all Americans .. it doesn’t mean that we’re not going to try to figure out how to protect our national security.”
-SOURCE: AP NEWS
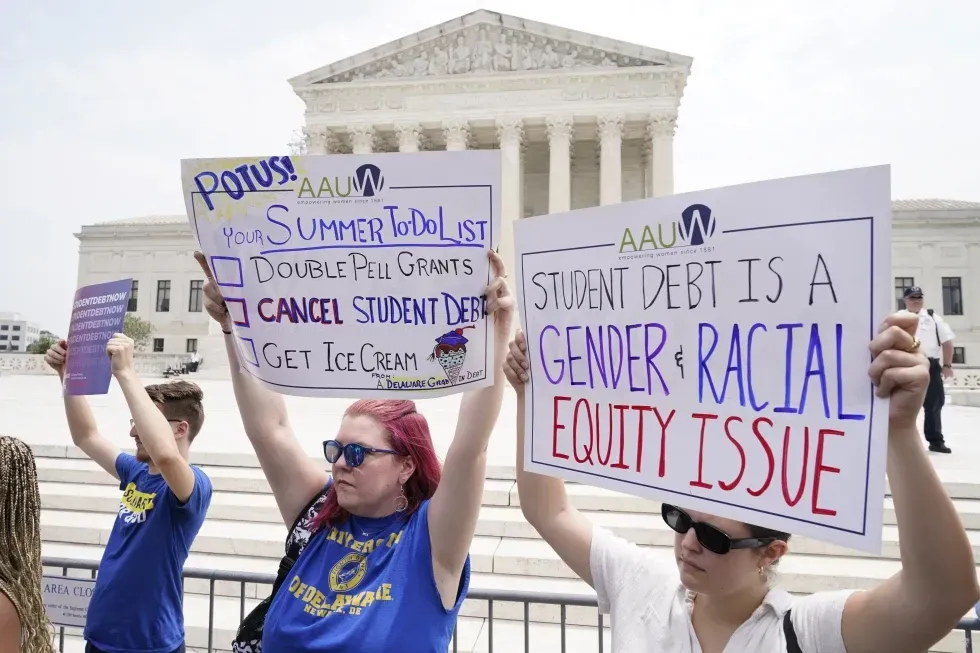
Savannah Britt owes about $27,000 on loans she took out to attend college at Rutgers University, a debt she was hoping to see reduced by President Joe Biden’s student loan forgiveness efforts.
Her payments are currently on hold while courts untangle challenges to the loan forgiveness program. But as the weeks tick down on Biden’s time in office, she could soon face a monthly payment of up to $250.
“With this new administration , the dream is gone. It’s shot,” said Britt, 30, who runs her own communications agency. “I was hopeful before Tuesday. I was waiting out the process. Even my mom has a loan that she took out to support me. She owes about $18,000, and she was in the process of it being forgiven, but it’s at a standstill.”
President-elect Donald Trump
and his fellow Republicans have criticized Biden’s loan forgiveness efforts, and lawsuits by GOP-led states have held up plans for widespread debt cancellation. Trump has not said what he would do on loan forgiveness, leaving millions of borrowers facing uncertainty over their personal finances.
The economy
was an important issue in the election, helping to propel Trump to victory. But for borrowers, concerns about their finances extend beyond inflation to include their student debt, said Persis Yu, managing counsel for the Student Borrower Protection Center.
“That’s a big part of what is making life unaffordable for them is this burden of expenses that they can’t seem to get out from under,” Yu said.
Student loan cancellation was not a focus of the campaign for either Trump or Vice President Kamala Harris , who steered clear of the issue at her political events. The issue came up just once in the September presidential debate, when Trump hammered Harris and Biden for failing to deliver their promise of widespread forgiveness. Trump called it a “total catastrophe” that “taunted young people.”
Biden promised the student loan cancellation program during his run for the presidency. From its launch, Biden’s loan forgiveness faced relentless pushback from opponents who said it heaped advantage on elites and came at the expense of those who repaid their loans or did not attend college.
Biden’s first plan to cancel up to $20,000 for millions of people was blocked by the Supreme Court last year. A second, narrower plan has been halted by a federal judge after Republican-led states sued. A separate policy intended to lower loan payments for struggling borrowers has been paused by a judge, also after Republican-controlled states challenged it.
Overall, Biden’s efforts were relatively unpopular, even among those with student loans. Three in 10 U.S. adults said they approved of how Biden had handled student loan debt, according to a poll this spring from the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy and The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research . Four in 10 disapproved. The others were neutral or didn’t know enough to say.
Project 2025, the blueprint for a hard-right turn in American government that aligns with some Trump priorities , calls for getting the federal government out of the student loan business and doing away with repayment plans that pre-date the Biden administration.
Even without directly addressing student loans, Trump has made promises that would affect them. He has pledged to eliminate the U.S. Department of Education, which manages the $1.6 trillion federal student loan portfolio. It’s unclear which entity would take that responsibility if the department were eliminated, which would require approval from Congress.Yu noted the Biden administration managed to cancel student loans for about 5 million borrowers , even though the signature forgiveness effort has been blocked. The administration did it by leaning into loan cancellation programs already in effect. For example, an existing student loan forgiveness program for public service workers has granted relief to more than 1 million Americans, up from just 7,000 who were approved before it was updated by the Biden administration two years ago.
“A lot of the cancellation that we saw in the last couple of years was because the Biden administration was committed to making the programs that are actually enshrined in law work for people,” Yu said.
The challenge of repaying the $23,000 she has borrowed to study education policy at Columbia University weighs on 23-year-old Zaakirah Rahman, but she said she did not see an alternative to pursing an advanced degree.
“It feels like the threshold for things is getting higher and suddenly getting a bachelor’s degree isn’t enough,” she said. “It’s expensive. It’s super expensive. But it seems like you don’t really have a choice.”
Sabrina Calazans, 27, owes about $30,000 on federal student loans from her college days at Arcadia University in Pennsylvania. Her payments also have been on hold, but she could soon face a monthly payment of over $300.
“As a first-generation American, I live at home with my family, I contribute to our household finances, and that payment is a lot for me and so many others like me,” said Calazans, who is originally from Brazil.
In her role as managing director for Student Debt Crisis Center, Calazans said she has been telling people to stay up to date on developments by using the loan simulator on the Federal Student Aid website and reading updated information on forgiveness qualifications and repayment programs.
“There’s a lot of confusion about student loans,” Calazans said, and not just among young people. “We’re seeing a lot of parents take out more debt for their children to be able to go to school. We’re seeing older folks go back to school and having to take out loans as well.”
SOURCE: AP NEWS

U.S. stocks are rallying Tuesday as voters head to the polls on the last day of the presidential election and as more data piles up showing the economy remains solid.
The S&P 500 was up 1.2% in afternoon trading, rising closer to its record set last month . The Dow Jones Industrial Average was up 431 points, or 1%, as of 12:50 p.m. Eastern time, while the Nasdaq composite was 1.5% higher.
Treasury yields also rallied after a report showed growth for retailers, transportation companies and other businesses in the U.S. services industries accelerated last month. That was despite economists’ expectations for a slowdown, and the Institute for Supply Management said it was the strongest growth since July 2022.
The strong data offered more hope that the U.S. economy will remain solid
and avoid a long-feared recession
following the worst inflation in generations
.
Excitement about the artificial-intelligence boom also helped lift the stock market, as it has for much of the last year. Software company Palantir Technologies jumped 23% after delivering bigger profit and revenue than analysts expected for the latest quarter. It’s an industry known for thinking and talking big, and CEO Alexander Karp said, “We absolutely eviscerated this quarter, driven by unrelenting AI demand that won’t slow down.”
It helped offset a 6.3% drop for NXP Semiconductors. The Dutch company fell to one of the largest losses in the S&P 500 after warning that weakness it saw in the industrial and other markets during the latest quarter is spreading to Europe and the Americas.
The market’s main event, though, is the election, even if the result may not be known for days, weeks or months as officials count all the votes. Such uncertainty could upset markets, along with an upcoming meeting by the Federal Reserve on interest rates later this week. The widespread expectation is for it to cut its main interest rate for a second straight time, as it widens its focus to keeping the job market solid in addition to getting inflation under control.
Despite all the uncertainty heading into the final day of voting, many professional investors suggest keeping the focus on the long term and what corporate profits will do over the next few years and a decade. The broad U.S. stock market has historically tended to rise regardless of which party wins the White House, even if each party’s policies help and hurt different industries’ profits underneath the surface.
Since 1945, the S&P 500 has risen in 73% of the years where a Democrat was president and 70% of the years when a Republican was the nation’s chief executive, according to Sam Stovall, chief investment strategist at CFRA.
The U.S. stock market has tended to rise more in magnitude when Democrats have been president, in part because a loss under George W. Bush’s term hurt the Republican’s average. Bush took over as the dot-com bubble was deflating and exited office when the 2008 global financial crisis and Great Recession were devastating markets.
The S&P 500 ended up rising 69.6% from that Election Day in 2020 through Monday, following President Joe Biden’s win. It set its latest all-time high on Oct. 18, as the U.S. economy bounced back from the COVID-19 pandemic and managed to avoid a recession despite a jump in inflation.
In the prior four years, the S&P 500 rose 57.5% from Election Day 2016 through Election Day 2020, in part because of cuts to tax rates signed by Trump.
Investors have already made moves in anticipation of a win by either Trump or Vice President Kamala Harris. The value of the Mexican peso might fall if Trump’s tariffs on Mexico come to fruition, for example.
But Paul Christopher, head of global investment strategy at Wells Fargo Investment Institute, suggests not getting caught up in the pre-election moves, or even those immediately after the polls close, “which we believe will face inevitable tempering, if not outright reversals, either before or after Inauguration Day.”
In the bond market, the yield on the 10-year Treasury rose to 4.34% following Tuesday morning’s strong report on U.S services businesses from 4.29% late Monday.
In stock markets abroad, indexes were mixed in Europe and Asia. The moves were mostly modest outside of jumps of 2.3% in Shanghai and 2.1% in Hong Kong.

Some manufacturers and retailers are urging President Joe Biden to invoke a 1947 law as a way to suspend a strike by 45,000 dockworkers that has shut down 36 U.S. ports from Maine to Texas.
At issue is Section 206 of the Labor Management Relations Act of 1947, better known as the Taft-Hartley Act. The law authorizes a president to seek a court order for an 80-day cooling-off period for companies and unions to try to resolve their differences.
Biden has said, though, that he won’t intervene in the strike.
Taft-Hartley was meant to curb the power of unions
The law was introduced by two Republicans — Sen. Robert Taft of Ohio and Rep. Fred Hartley Jr. of New Jersey — in the aftermath of World War II. It followed a series of strikes in 1945 and 1946 by workers who demanded better pay and working conditions after the privations of wartime.
President Harry Truman opposed Taft-Hartley, but his veto was overridden by Congress.
In addition to authorizing a president to intervene in strikes, the law banned “closed shops,” which require employers to hire only union workers. The ban allowed workers to refuse to join a union.
Taft-Hartley also barred “secondary boycotts,’' thereby making it illegal for unions to pressure neutral companies to stop doing business with an employer that was targeted in a strike.
It also required union leaders to sign affidavits declaring that they did not support the Communist Party.
Presidents can target a strike that may “imperil the national health and safety”
The president can appoint a board of inquiry to review and write a report on the labor dispute — and then direct the attorney general to ask a federal court to suspend a strike by workers or a lockout by management.
If the court issues an injunction, an 80-day cooling-off period would begin. During this period, management and unions must ”make every effort to adjust and settle their differences.’'
Still, the law cannot actually force union members to accept a contract offer.
Presidents have invoked Taft-Hartley 37 times in labor disputes
According to the Congressional Research Service, about half the time that presidents have invoked Section 206 of Taft-Hartley, the parties worked out their differences. But nine times, according to the research service, the workers went ahead with a strike.
President George W. Bush invoked Taft-Hartley in 2002 after 29 West Coast ports locked out members of the International Longshore and Warehouse Union in a standoff. (The two sides ended up reaching a contract.)
Biden has said he won’t use Taft-Hartley to intervene
Despite lobbying by the National Association of Manufacturers and the National Retail Federation, the president has maintained that he has no plans to try to suspend the dockworkers’ strike against ports on the East and Gulf coasts.
On Wednesday, before leaving Joint Base Andrews for an air tour of North Carolina to see the devastation from Hurricane Helene, Biden said the port strike was hampering efforts to provide emergency items for the relief effort.
“This natural disaster is incredibly consequential,” the president said. “The last thing we need on top of that is a man-made disaster — what’s going on at the ports.”
Biden noted that the companies that control East and Gulf coast ports have made huge profits since the pandemic.
“It’s time for them to sit at the table and get this strike done,” he said.
Though many ports are publicly owned, private companies often run operations that load and unload cargo.
William Brucher, a labor relations expert at Rutgers University, notes that Taft-Hartley injunctions are “widely despised, if not universally despised, by labor unions in the United States.”
And Vice President Kamala Harris is relying on support from organized labor in her presidential campaign against Donald Trump.
If the longshoremen’s strike drags on long enough and causes shortages that antagonize American consumers, pressure could grow on Biden to change course and intervene. But experts like Brucher suggest that most voters have already made up their minds and that the election outcome is “really more about turnout” now.
Which means, Brucher said, that “Democrats really can’t afford to alienate organized labor.”

